Solar-Powered Greenhouse: Energy-Efficient Farming for the Future
As the world shifts toward sustainability, solar-powered greenhouses are emerging as a forward-thinking solution for energy-efficient farming. By harnessing the sun’s abundant energy, these innovative systems reduce operational costs, minimize environmental impact, and ensure year-round crop production. In this blog, we’ll explore how solar-powered greenhouses work, their benefits, and why they’re shaping the future of agriculture.
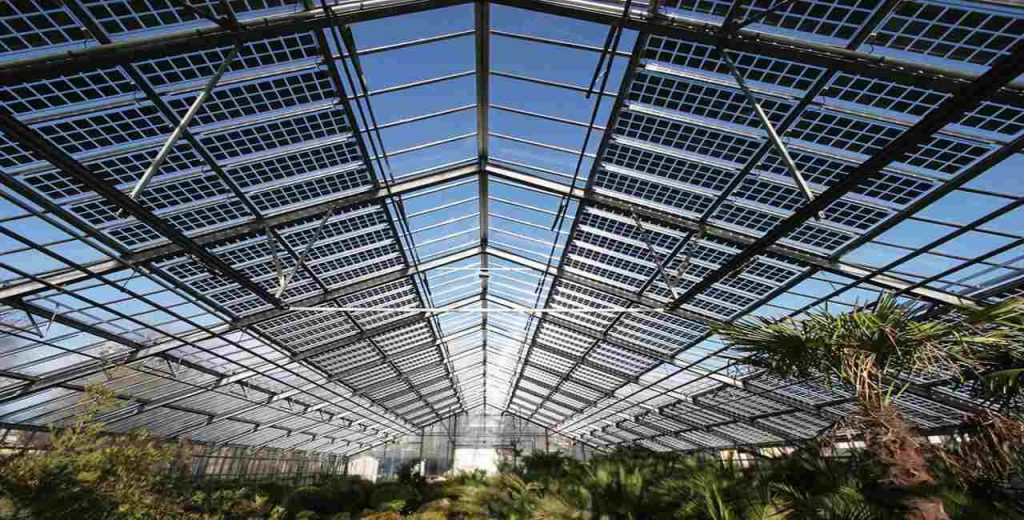

What is a Solar-Powered Greenhouse?
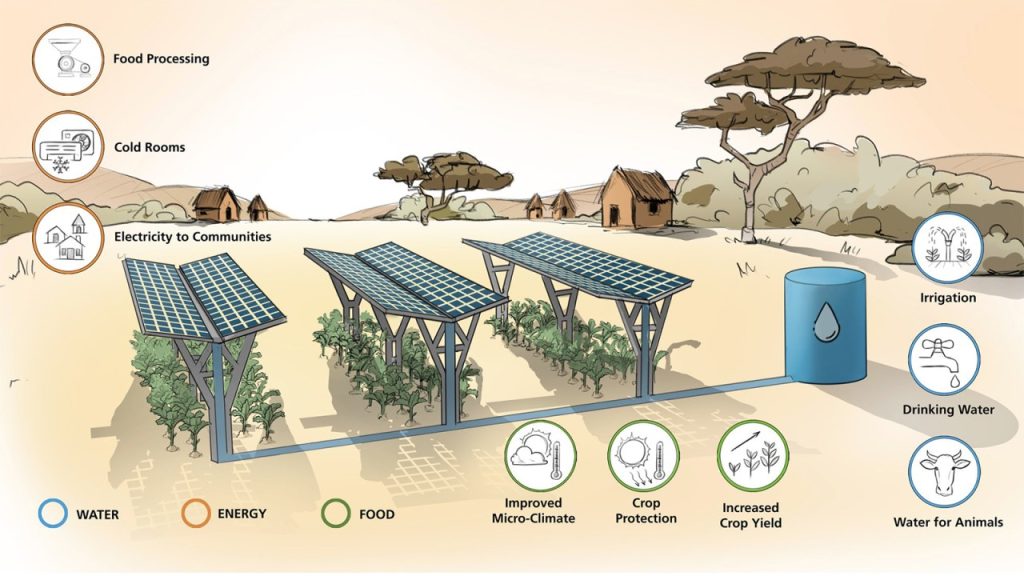
A solar-powered greenhouse is a farm building powered mainly by solar energy. With solar panels, the greenhouses harvest sunlight and turn it into electricity to power critical systems such as heating, cooling, lighting, and irrigation. This green energy method makes them environmentally friendly and economical, providing a renewable option compared to conventional greenhouses powered by fossil fuels or grid electricity.
How Solar Power Boosts Greenhouse Efficiency
Solar power complements greenhouse functions nicely by driving principal components while minimizing reliance on outside power. Here’s the process:
- Solar Panels: Photovoltaic (PV) panels placed on the rooftop or surrounding areas harvest sunlight and convert it into electricity.
- Energy Storage: Batteries retain surplus energy generated during the day for nighttime or cloudy days to keep the operation going on.
- Temperature control: Solar energy supplies heaters, fans, or evaporative coolers to achieve the perfect temperatures.
- Lighting: Solar-powered energy-efficient LED grow lights promote plant growth during winter months when there is less light.
- Irrigation: Solar-powered pumps supply water to plants, saving manual labor and resources.
Solar-powered greenhouses save high electricity bills and cut greenhouse gas emissions by utilizing clean energy.
Components of a Solar-Powered Greenhouse
Component | Function | Energy Source |
Solar Panels | Generate electricity from sunlight | Solar Energy |
Batteries | Store excess energy for later use | Solar Energy |
Heating/Cooling | Regulate temperature | Solar-Powered |
LED Lighting | Support plant growth in low light | Solar-Powered |
Irrigation Pumps | Deliver water to plants | Solar-Powered |
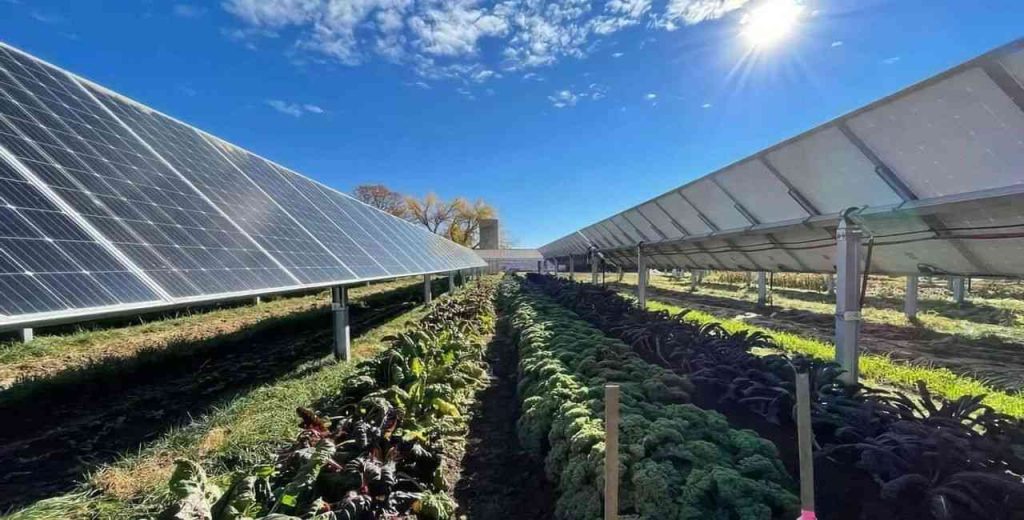

Key Benefits of Solar-Powered Greenhouses
Switching to solar energy offers a range of advantages for farmers and the environment:
- Energy Cost Savings: After the initial investment, solar power significantly lowers utility expenses, making farming more profitable.
- Sustainability: Solar energy is renewable and reduces the carbon footprint of agricultural operations.
- Year-Round Production: Stored solar energy ensures consistent climate control, enabling crop growth in any season or climate.
- Off-Grid Capability: Solar greenhouses can operate in remote areas without access to the power grid, expanding farming opportunities.
- Low Maintenance: Solar panels require minimal upkeep and have a lifespan of 20-30 years, offering long-term reliability.
Benefits of Solar-Powered Greenhouses
Benefit | Description | Impact |
Energy Cost Savings | Reduces utility bills over time | Increased Profitability |
Sustainability | Uses renewable energy, lowers emissions | Eco-Friendly |
Year-Round Production | Enables consistent crop growth | Higher Yields |
Off-Grid Capability | Operates without grid access | Expanded Reach |
Low Maintenance | Long lifespan with minimal upkeep | Cost-Effective |
Combining Solar Power with Smart Technology
To maximize efficiency, solar-powered greenhouses often use smart technology such as automation and sensors. These utilize energy more efficiently by:
- Measuring light intensity to control artificial lighting.
- Sustaining temperature and humidity with solar-powered climate control.
- Controlling irrigation using soil moisture readings.
This combination of solar power and smart technology provides a self-sustaining, high-performing growing space.
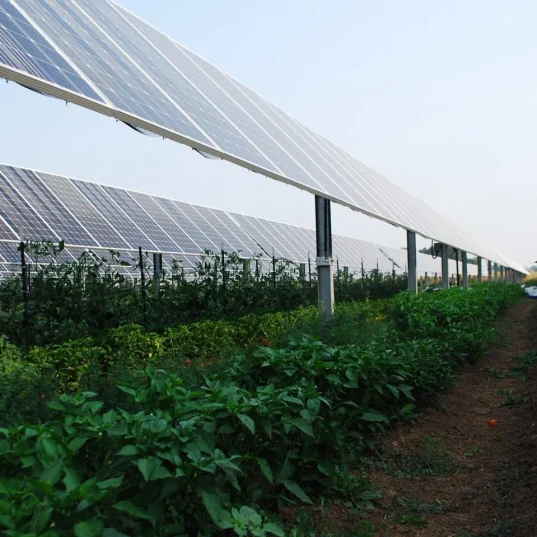


Why Solar-Powered Greenhouses Are the Future
The agriculture industry is confronted with increasing challenges, from increased energy prices to climatic uncertainty. Solar greenhouses meet these challenges head-on by providing a scalable, environmentally friendly solution. They enable farmers to grow fresh, local produce sustainably and decrease dependence on non-renewable resources. Governments and institutions are also encouraging solar adoption through grants and tax incentives, facilitating growers to switch over.
Challenges to Consider
Although solar-powered greenhouses are extremely useful, there are some things to remember:
- Initial Expenses: Solar panel and battery installation involves an initial cost, although long-term benefits pay for it.
- Space Needs: Proper space for panels is necessary, which could be a drawback for small installations.
- Weather Conditions: Regions that receive low sun exposure can need more frequent battery storage or hybrid units to provide power continuity
Challenges of Solar-Powered Greenhouses
Challenge | Description | Solution |
Upfront Costs | High initial investment | Long-term savings, incentives |
Space Requirements | Needs area for solar panels | Compact designs, land planning |
Weather Dependency | Reduced efficiency in cloudy areas | Battery storage, hybrid systems |
Despite these challenges, advancements in solar technology are making it more accessible and efficient every year.
Conclusion
Solar-powered greenhouses represent the future of energy-efficient farming, blending renewable energy with modern agriculture. By reducing costs, enhancing sustainability, and enabling consistent production, they offer a practical path toward a greener planet. Whether you’re a hobbyist gardener or a commercial farmer, exploring solar-powered greenhouse options can set you up for success in an eco-conscious world.











Add comment